
VSEPR Theory Postulates: The VSEPR theory postulates are mentioned below: When there are no unpaired electrons in a chemical, the molecule and electron pairs of the chemical are the same. Molecular and electron pair geometry differ in the sense that molecular geometry eliminates non-paired electrons, whereas electron pair geometries comprise both unpaired and bound atoms. The angle formed by a bound atom, the center atom, and another bonded atom is the bond angle.Ī pair of valence electrons not shared with another atom is called a lone pair.Ī polyatomic ion or molecule features a 3-D arrangement of atoms bound by their bonds.Īn electron-pair geometry is the structure of electron pairs around a molecule or ion’s core atom. The following terminologies can be applied while describing molecular shapes. This hypothesis is sometimes known as the Gillespie-Nyholm theory to honor these chemists.Īccording to the VSEPR theory/ shape of SF4 according to VSEPR theory, the Pauli exclusion principle causes the repulsion between two electrons, which is more critical than electrostatic repulsion to determine the structure of molecules. Ronald Nyholm and Ronald Gillespie are the two key founders of the VSEPR hypothesis. Each form is assigned a name and an ideal bond angle. The VSEPR model assumes that electrons orbiting an atom, position themselves in such a way as to minimize repulsion, thereby determining its molecular structure.Īs long as the central atom is not a metal, it can predict the form of practically all compounds with a central atom. The VSEPR model accurately predicts the 3-D shape of molecules and ions, but it fails to provide any detailed information on link length or bond structure.
VSEPR Models’ Importanceīecause Lewis structures limit themselves to two dimensions, they can only tell you how many and what kinds of links exist between atoms.

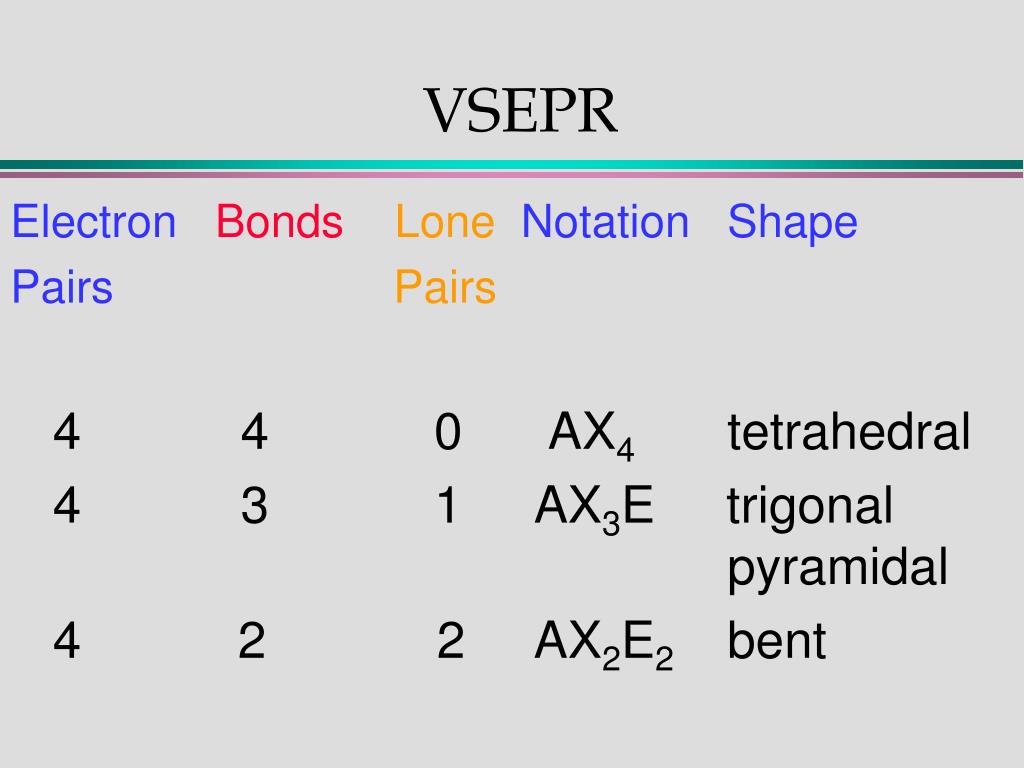
Therefore, the molecule loses energy and becomes more stable, which determines its molecular geometry. Therefore, they will adopt configurations that minimize this repulsion. The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR theory) relies on the idea that there is repulsion between the valence electron pairs surrounding an atom. All positions are chemically equivalent, so all electronic interactions are equivalent.What is VSEPR Theory, and how does it work? (This rule is more important than rule 1, so it overrules it because it has lone pairs. From Figure \(\PageIndex\) can result from differences in repulsion between various regions of electron density. Other interactions, such as nuclear-nuclear repulsions and nuclear-electron attractions, are also involved in the final arrangement that atoms adopt in a particular molecular structure. The model states that electron pairs will repel each other such that the shape of the molecule will adjust so that the valence electron-pairs stay as far apart from each other as possible. The central atom, sulfur, has 6 valence electrons, as does each oxygen atom. What are the electron-pair geometry and molecular structure of this polyatomic ion? Answers will vary. In an octahedral arrangement with two lone pairs, repulsion is minimized when the lone pairs are on opposite sides of the central atom. Click the card to flip Flashcards Learn Test Match Created by Andrea636 Terms in this set (27) Valence In addition, there was significant damage to livestock and crops. Therefore, we can draw a cross bow arrow towards Oxygen. The cross base arrow demonstrates the net dipole. VSEPR focuses not only on electron pairs, but it also focus on electron groups as a whole. The basic geometry is trigonal planar with 120 bond angles, but we see that the double bond causes slightly larger angles (121), and the angle between the single bonds is slightly smaller (118). Generally, a negative person is seen as bad or mean and you don't want to talk to a negative person. It is useful for nearly all compounds that have a central atom that is not a metal. Which molecule(s) has a net dipole moment? We need to comprehend electronegativity which is abbreviated EN. When drawing covalent molecules, remember that the electrons are shared between two atoms, forming a covalent bond. What is the VSEPR Theory? O lone pairs only.
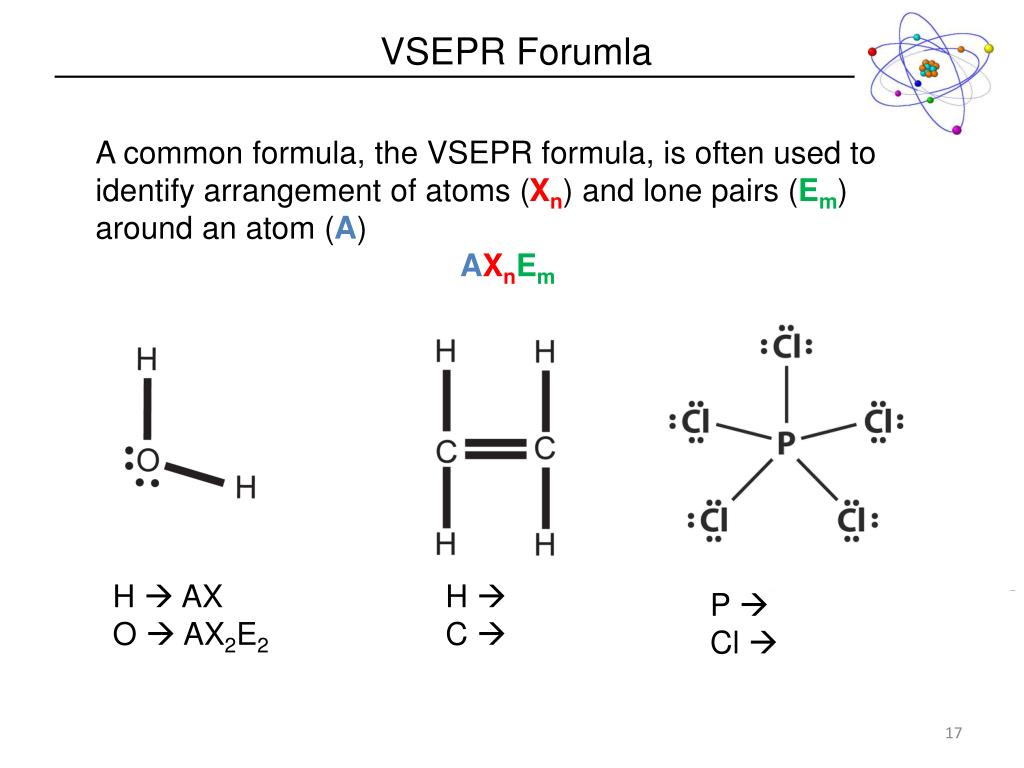
In the VSEPR model, the molecule or polyatomic ion is given an AXmEn designation, where A is the central atom, X is a bonded atom, E is a nonbonding valence electron group (usually a lone pair of electrons), and m and n are integers. On the cross-base arrow, the cross represents the positive charge and the arrow represents the negative charge. Then, with the Lewis structure, we apply the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSPER) theory to determine the molecular geometry and the electron-group geometry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
